Geocoding. Efficient geolocation thanks to complete data.
Enrich your address data with geo-coordinates and calculate exact distances and directions and see exactly where your customers live and stay. For successful georeferenced marketing.


Quick Facts about our geocoding solution:
- Flexible geographic and micromarketing data enrichment.
- Available on premise, in the cloud and as a service.
- International solution approach. Worldwide data available.
- Fast and straightforward implementation.
Every address precisely on every map in every system.
With Uniserv Geocoding, you receive a tool which spatially locates the addresses of your customers and relates them to external market data (e.g. sociodemographic or socioeconomic structural characteristics) in order to create a basis for entrepreneurial decisions. You gain additional knowledge about the addresses of your customers and prospects worldwide. Whether B2B or B2C, companies in all industries benefit from modern sales, marketing and expansion planning with geocoding.
Our software cost-effectively links your customer and address data with important geographical characteristics worldwide, thereby providing the basis for successful location planning, target group, potential and competition analysis, microgeographic market segmentation, and service and sales optimization, among other things. This is the basis for future strategic business decisions. The prerequisite for this is professional and automated data management.
Uniserv geocoding helps you find answers to the following questions:
- How many customers live in the catchment area of location X?
- Which factors influence the success of my locations?
- Where are the white spots for my expansion?
- How much revenue can I generate at a location?
- How many customers will I gain by opening a new location?
- Where would my locations be optimally placed?
- How do I optimize supply and logistics processes?
- What potential customer losses result from site closures?
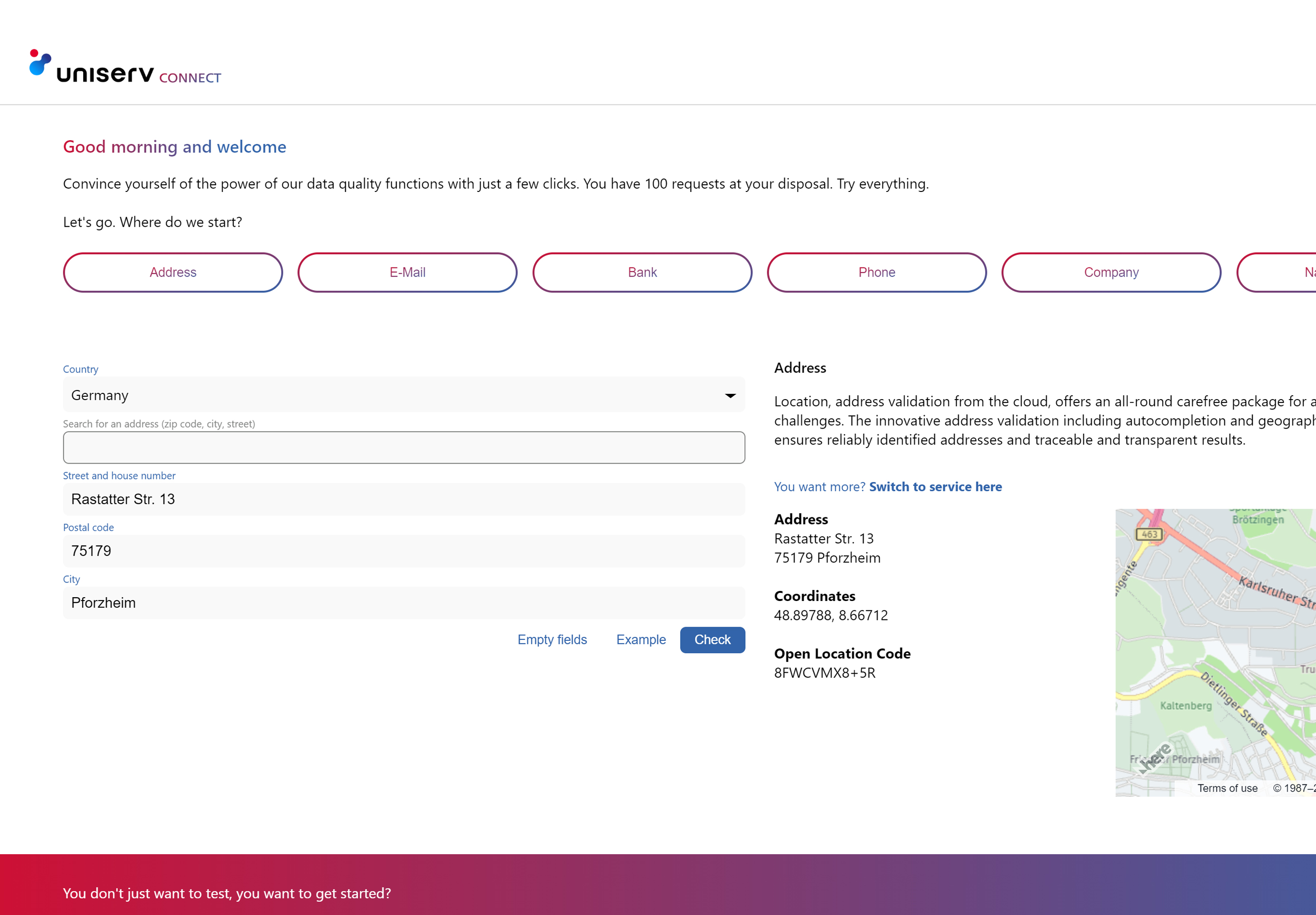
Check it out & try our geocoding solution
Test and discover our Data Quality Services from the cloud in Uniserv CONNECT free of charge and without obligation. Interactively check address, contact, company and bank data. What to expect:
- 100 free requests. Test all services extensively & free of charge.
- API documentation. All integration & interface details.
- Discover & try out. Clear examples of different use cases.
- Questions? Our experts are ready to help you.
Case study
Optimization of sales territories and dealer networks using the example of an industrial company
Today, industrial companies depend on a first-class sales force that adapts its structure, processes and dealer networks to rapidly changing market conditions. Geographical analyses help by showing market penetration - overall as well as by divisions and individual products. Competitive analyses complete the results and help to understand the competition. As a sales department, you can quickly assess where the greatest opportunities for growth exist. Based on the results of the geoanalyses, you as an industrial company not only optimize existing territories. You also build new territory structures for entering new markets and for product expansions. Sales territories can be optimized according to potential, workload and routes. Ideal structures ensure that your sales representatives in the field spend their time with the most promising customers instead of on the road.

Uniserv Geocoding offers you the following services:
- Creation of correct customer master data through postal verification.
- Linking with geographic coordinates (geocoordinates).
- Key to micromarketing data, such as statements about the residential environment, income, consumer behavior or age structure.
With the help of this data, you can locate your customers in space, link your company's own key figures with differentiated market and potential data, and condense your customer master data into a comprehensive 360° view of your customer - the Golden Profile is created. The data can be assigned in a targeted manner for an individual house, a street section, a street, a district or for a complete town. The geo-information can be assigned directly when the address is entered, or it can be conveniently added to large databases in batches. A uniform interface design simplifies the integration of country-specific geo-information. The considerable differences in the available information are thus compensated for. This minimizes the costs for integration into existing systems and provides the basis for "borderless" address geocoding. Uniserv Geocoding links customer master data with geographical characteristics from over 240 countries. The national product variants of the software take into account the respective country-specific conditions and requirements for address geocoding.
FAQs
Geocoding is a process that allows geographic information to be associated with an address or a known location. Geographic information is often geographic coordinates, but also socio-demographic data, statistical data on the environment and weather, and any other form of data with a spatial reference.
Geocoding is a vehicle, a bridge, to make addresses more valuable, i.e. more meaningful. The geo-coordinates serve as a link between the pure address and additional information, with the help of which an address can be enriched with additional information. This expands the range of uses of an address.
Reverse geocoding means that a building or a named place in the vicinity is assigned to a coordinate.
Geocoding with shapefiles is an extension of geocoding. A shapefile is a data structure that describes a geographical area via a list of connected corner points (polygon course). This makes it possible to use an assigned coordinate to decide for each address in which geographical area it is located.
Geofencing is another important sub-area of geocoding. Geofencing is a made-up word from the English terms geographic and fence. It means the digital implementation of a boundary line, often as a closed area, the crossing of which triggers an action. In the simplest case, the boundary line can be a circle or rectangle, but in more sophisticated cases it can also be a complex polygon in the form of a shapefile.
Geomarketing is the classic field of application for geocoding. With the help of statistical data on social background and buying behaviour, target groups for campaigns are selected according to geographical criteria or interested parties are classified at an early stage and addressed in a differentiated manner. In the context of an increasingly personalised approach to prospective customers, the segmentations that traditional geomarketing allows are in many cases too coarse on their own.
At first glance, route planning for delivery services looks like a navigation system, but on closer inspection it turns out to be much more complex. Here, not only a route between a starting point and a destination must be determined, but a route that optimally connects a series of predefined approach points. Additional geocoding information can be used to further optimise route planning. For example, taking into account the information whether a building is used for business or private purposes in the route planning can help to increase the probability of a delivery being made.
Different geocoding information is used for location planning for retail chains. With the means of classic geomarketing (e.g. socio-demographic data), it can be determined where the target group for a certain offer predominantly lives. A low-price offer must be accessible to other target groups compared to an offer in the high-price segment. A new branch must be easily accessible for the addressed target group. For this purpose, data on street routes must be included in addition to spatial proximity. It is not enough that the residential areas of the target group and the branch are close to each other if both are separated by a motorway and the next bridge over the motorway is several kilometres away.
The automatic assignment of an interested party to the responsible sales agent within the framework of a regional sales structure can take place according to different criteria. In the simplest case, spatial proximity can be used as a characteristic. Based on the geographical position of the sales agents' locations and the geocoded address of the interested party, the sales agent with the smallest distance to the interested party is selected. Geographically defined sales territories (e.g. in the form of shapefiles) are an alternative. They can be optimised based on criteria such as accessibility and sales potential. Using a shapefile geocoding, the prospect is then assigned to the corresponding sales area based on his geocoded address. The same procedures are also applicable when assigning a prospect who registers in an online portal to a sales branch.
Location-based mobile marketing is about identifying a potential customer in the vicinity of a branch and then luring them into the branch with a special offer. To realise this, a mobile app and geo-fencing are usually used. The app provides the current coordinates of the mobile device and the geo-fencing triggers the activating offer for the customer. This can be, for example, an attractive voucher that is displayed via the app. The prerequisite is the geocoding of all possible branches with geographical coordinates.
The reference data are decisive for the quality of the geocoding. Depending on the origin of the reference data, there are differences in completeness, correctness, accuracy and topicality.
The degree of completeness indicates the relative proportion of buildings or places that are recorded in the reference data. If buildings are missing in the reference data, then the corresponding addresses cannot be geocoded at all or only with a lower accuracy.
The correctness of the reference data indicates the extent to which the information on addresses and places matches the common names (as used for places, municipalities, subdivisions and streets). These are primarily the official place and street names as they appear on street signs, for example. However, these are also common synonyms or short spellings that are frequently used. Only if the spelling in the reference data is correct can a highly automated assignment of geocoding information take place.
The accuracy of the reference data indicates the level at which the assignment to an address is actually made. For example, coordinates can be measured exactly for a building or interpolated from buildings "nearby". In extreme cases, they only indicate the centre of the street or municipality in which the building is located. For socio-demographic data, data protection in Germany defines a maximum accuracy that must not be exceeded in order to prevent conclusions being drawn about individual persons. Which accuracy is required in each case depends entirely on the application.
The timeliness of reference data describes how quickly changes in the real world find their way into the reference data. Completeness and correctness always apply to a specific point in time. Newly created streets and buildings mean that the completeness of reference data continues to decrease if the corresponding information is not repeatedly researched and supplemented. Renaming of streets and incorporations mean that once correct address information in the reference data does not automatically remain correct in the long term. Changes must be regularly recorded and the corresponding data updated.
You might also be interested in: